The Gold-Salt Trade
Made by Alex Huerta and Jimmy Washington
Driving Question:
How did the Gold-Salt Trade connect communities?
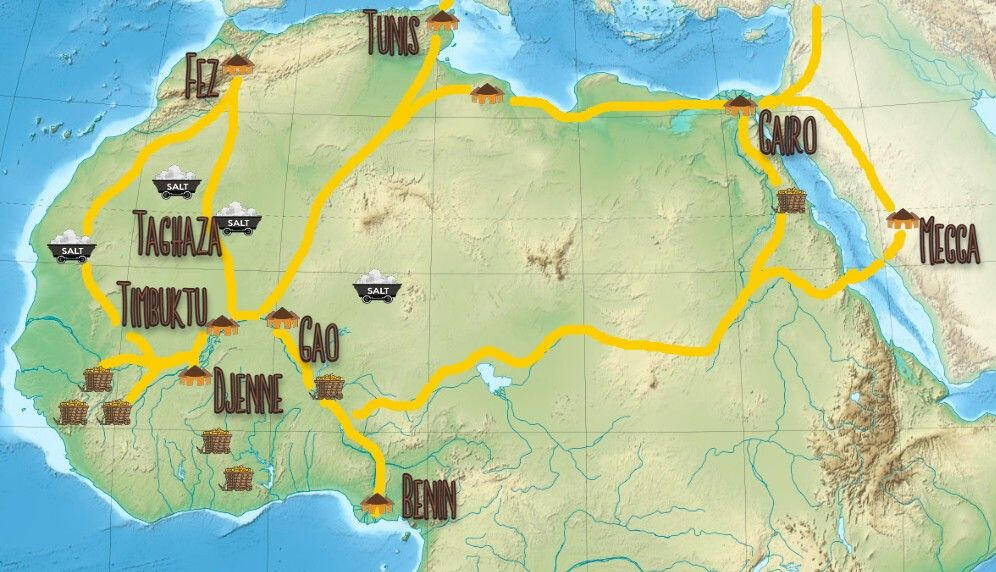
The Gold-Salt Trade allowed different civilizations to exchange goods, ideas and culture, while also shaping the economy, societies and the culture. "The routes then extended north through salt mining towns like Taghaza before reaching the Mediterranean coastal cities of North Africa, such as Tunis and Tripoli. From there, goods were traded into Europe, the Middle East, and Asia."
Alex Source
The Sahara desert was a natural barrier that divided sub-Saharan Africa from the barbers. Even with this geological factor, trade still flourished in this region due to the Sahara having oases and camels to make the journey more tolerable and the terrain traversable.

Jimmy Source
The Gold-Salt Trade allowed Berber nomads from the north to interact with the Timbuktu and Djenné, which allowed the exchange of ideas, languages, and beliefs like Islam. "...Berbers and the Tuareg came into their own as a means to cross the dangerous and inhospitable Sahara and acquire the precious metal from Africa's interior and bring it back to such cities as Marrakesh, Fez, Tunis, and Cairo."
Alex Source
The gold and salt trade routes were important trade network lanes that connected sub-saharan West Africa with the Middle East and Europe. This connection also made states in West Africa incredibly wealthy when they had control over the mines and trade routes.

Jimmy Source
The Gold-Salt Trade allowed the Mediterranean and the sub-Saharan economies to be linked, due to the the demand of gold and salt. "Increased demand for gold in the North Islamic states, which sought the raw metal for minting, prompted scholarly attention to Mali and Ghana...By 1050, Ghana was strong enough to assume control of the Islamic Berber town of Audaghost."
Alex Source
References Cartwright, Mark. 2019. “The Gold Trade of Ancient & Medieval West Africa.” World History. https://www.worldhistory.org/article/1383/the-gold-trade-of-ancient--medieval-west-africa/. Department of Arts of Africa, Oceania, and the Americas. 2000. “The Trans-Saharan Gold Trade (7th–14th Century).” Met Museum. https://www.metmuseum.org/essays/the-trans-saharan-gold-trade-7th-14th-century. “Gold & Salt Trade in Africa | Definition, Difficulties & History.” n.d. Study. https://study.com/academy/lesson/gold-and-salt-trade-in-ancient-africa.html. “Medieval Trade Routes.” n.d. Hey Miss a World. https://heymissaworld.weebly.com/medieval-trade-routes.html. “The Trans-Saharan Gold-Salt Trade.” n.d. Students of History. https://www.studentsofhistory.com/trans-saharan-trade.